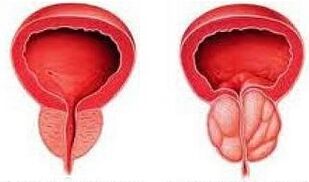
Chronic prostatitis is a long -term inflammation of the prostate gland, while symptoms are often absent, so the majority of the male population is not aware of the disease.

The development of a chronic form of prostatitis is a consequence of an acute process, although in practice this is quite rare.As a general rule, inflammatory chronic prostatitis begins gradually, without any unpleasant symptoms and sensations, often the course of the disease is in the patient by accident, when examining an ultrasound.Prostatitis also threatens those who lead an inactive lifestyle by the family of their activities, feel excessive physical effort in the crotch and observe sexual abstinence.In general, it is caused by a bacterial infection and is easily diagnosed due to the typical signs.Acute bacterial prostatitis can occur at any age.Symptoms include painful urine, the inability to completely empty the bladder, pain in the lower abdomen, back or pelvic area.There may be a fever accompanied by chills.
Clasificación
Según la clasificación moderna de la prostatitis, desarrollada en 1995, se distinguen varias categorías de la enfermedad:
- La prostatitis bacteriana aguda (OBP) es el tipo más común de prostatitis. Por lo general, es causado por una infección bacteriana y se diagnostica fácilmente debido a los signos típicos. La prostatitis bacteriana aguda puede ocurrir a cualquier edad. Los síntomas incluyen orina dolorosa, la incapacidad de vaciar por completo la vejiga, el dolor en la parte inferior del abdomen, la espalda o el área pélvica. Puede haber fiebre acompañada de escalofríos.
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a disease with typical symptoms of chronic inflammation and a greater amount of bacteria and leukocytes in the urine and the secret of the prostate after its massage.
- Chronic prostatitis (PC) is the most common form of prostatitis.In most cases, it is a consequence of acute bacterial prostatitis (not treated or poorly treated).If there are symptoms, then they occur in the form of pain in the genitals or in the pelvic area, difficulties during urination or painful urine and ejaculation.They indicate a chronic bacterial (infectious) prostatitis;In the absence of microbial pathogens, on non -bacterial (non -infectious) prostatitis.It is believed that in 90-95% of all cases, chronic non-bacterial prostatitis occurs and only in 10-5% -Bacteria.
En presencia de un componente infeccioso, indican una prostatitis crónica bacteriana (infecciosa); En ausencia de patógenos microbianos, sobre prostatitis no bacteriana (no infecciosa). Se cree que en el 90-95% de todos los casos, se produce prostatitis crónica no bacteriana y solo en 10-5%-bacterias.
Reasons
The appearance of chronic prostatitis can contribute to a series of factors.In the first place, this is:
- IPP: clamidia, ureplasma, mycoplasma, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, tricomonades, gocococcus, genu ado, e. coli (Escherichia coli) can affect the urethra and detect prostate in the tissue;
- stagnation in the prostate leads to its inflammation);Chronicle, not so much the presence and activity of the pathogens of microorganisms is important as the condition of the pelvis and blood circulation in them, the presence of concomitant diseases and the level of protective mechanisms.In this case, all the signs of acute prostatitis are not manifested or shown to a lesser extent.Very bright, they can be so insignificant that patients with chronic prostatitis do not pay much attention.
- Exacerbation of chronic prostatitis
- The exacerbation of the disease, as a rule, accompanies the following symptoms:
- Pain and ardor in the urethra;
- Frequent urgency to the urinary process;
Síntomas de prostatitis crónica
La mayoría de las veces, con el desarrollo de una forma crónica de prostatitis, los síntomas prácticamente sin molestar a un hombre. En este caso, todos los signos de prostatitis aguda no se manifiestan ni se mostrarán en menor medida.
Los síntomas más comunes de la prostatitis crónica en los hombres son:
- dolores periódicos y sensaciones desagradables en el perineo;
- sensaciones desagradables en defecación y micción;
- irradiación en el ano, muslo, testículos;
- Descargas de la uretra.
Los cambios en la imagen del curso de la enfermedad, ya no muy brillante, pueden ser tan insignificantes que los pacientes con prostatitis crónica no les prestan mucha atención.
Exacerbación de la prostatitis crónica
La exacerbación de la enfermedad, como regla, acompaña a los siguientes síntomas:
- dolor y ardor en la uretra;
- urgencia frecuente al proceso urinario;
- pain in the lower abdomen, perineum and rectum;
- signs of decrease in men of sexual activity;
- pain during the act of defecation.Only 2-3 signs of the disease.For example, the most common is a deteriorated erection and pain at the bottom of the abdomen.With inflammation, the secretory function of the prostate gland worsens, which inevitably affects the quality of sperm.

In addition, the prostate gland actively participates in the regulation of testosterone production and the erection process.That is why chronic prostatitis causes a decrease in erectile function, until impotence.However, these scenarios for the development of the disease can be avoided through timely and competent treatment.
DiagnosisUrodynamics are done additionally.
How to treat chronic prostatitis
If a man has chronic prostatitis, treatment is always long and difficult.Its duration depends directly on the stage of the disease in which the patient turned to a specialist.The therapy implies an integrated approach, that is, a combination of several methods simultaneously:
Antibacterial therapy;
Prostate massage;
Se necesitan los siguientes procedimientos para ayudar a establecer/refutar el diagnóstico:
- estudio rectal;
- microscopía del secreto de la próstata;
- siembra el secreto de la próstata para la sensibilidad a los antibióticos;
- enfermedades de transmisión sexual;
- Ultrasonido transrectal.
A veces, los estudios endoscópicos y urodinámicos se realizan adicionalmente.
Cómo tratar la prostatitis crónica
Si un hombre tiene prostatitis crónica, el tratamiento siempre es largo y difícil. Su duración depende directamente de la etapa de la enfermedad en la que el paciente recurrió a un especialista. La terapia implica un enfoque integrado, es decir, una combinación de varios métodos simultáneamente:
- terapia antibacteriana;
- masaje de próstata;
- procedimientos fisioterapéuticos;
- corrección de la dieta y el estilo de vida;
- el uso de remedios populares;
- Tratamiento quirúrgico.
In addition, anti -inflammatory and antispasmodic agents are used in the treatment of the chronic form of the disease.
Drug treatment
The choice of medications depends on the cause and symptoms of the disease.To cure chronic prostatitis of infectious etiology, antibacterial drugs are used:
- Fluoroquinolones;
- Macrolides;
- Tetracyclines.

To eliminate inflammatory phenomenPerform using medications that were not previously used for this purpose: ALFA1 blockers, inhibitors of 5 reds, cytokine inhibitors, immunosuppressants, drugs that affect the exchange of urrato and citrate.
Physiotherapy
Certain physiotherapeutic procedures, such as laser therapy, electrophoresis, microwave hyperthermia, ultrasonic phonophorem and others, also help improve the trophic tissues of the prostate and accelerate healing tissueReceptionProstate massage is usually combined with antibiotic therapy.Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the high effectiveness of this treatment.
Operation
Surgical intervention is possible to eliminate prostate areas affected by bacteria.Transurethral resection is an operation that is performed under epidural or intravenous barbiturate anesthesia.The postoperative recovery period does not last more than a week.Carrying out an independent therapy in the home based on internet reviews is full of consequences.
Mejora el drenaje del secreto de la próstata y la microcirculación a nivel de este órgano, lo que a su vez contribuye a la rápida recuperación del paciente.
El masaje de la próstata no se puede llevar a cabo con prostatitis aguda, hemorroides, grietas en el recto. El masaje de próstata generalmente se combina con terapia con antibióticos. Numerosos estudios clínicos han demostrado la alta efectividad de dicho tratamiento.
Operación
La intervención quirúrgica es posible para eliminar las áreas de próstata afectadas por bacterias. La resección transuretral es una operación que se realiza bajo anestesia barbitúrica epidural o intravenosa. El período de recuperación postoperatoria no dura más de una semana.
Los métodos que implican el tratamiento de la prostatitis crónica están determinados por el urólogo en función de la información de diagnóstico y su experiencia práctica. Llevar a cabo una terapia independiente en el hogar basada en revisiones en Internet está llena de consecuencias.